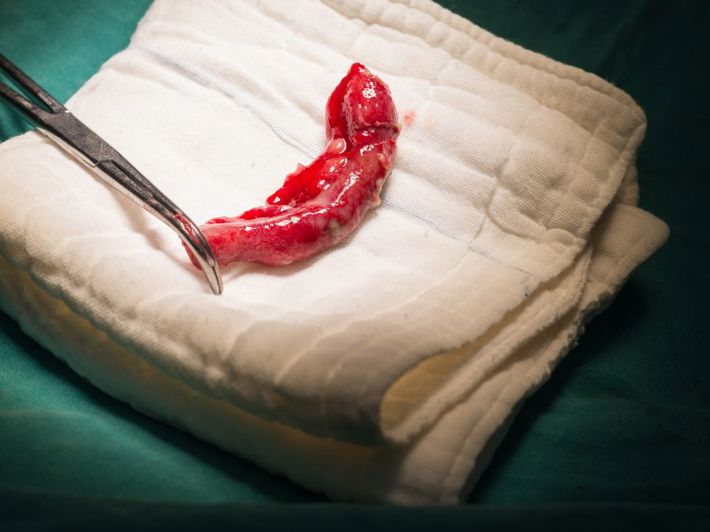
Appendectomy (appendix removal) is one of the most common emergency surgeries worldwide. It is performed to treat appendicitis, a condition where the appendix becomes inflamed. If untreated, the appendix can rupture, spreading bacteria and infection throughout the abdominal cavity, which can be life-threatening. (1)
What Is Laparoscopic Appendectomy?
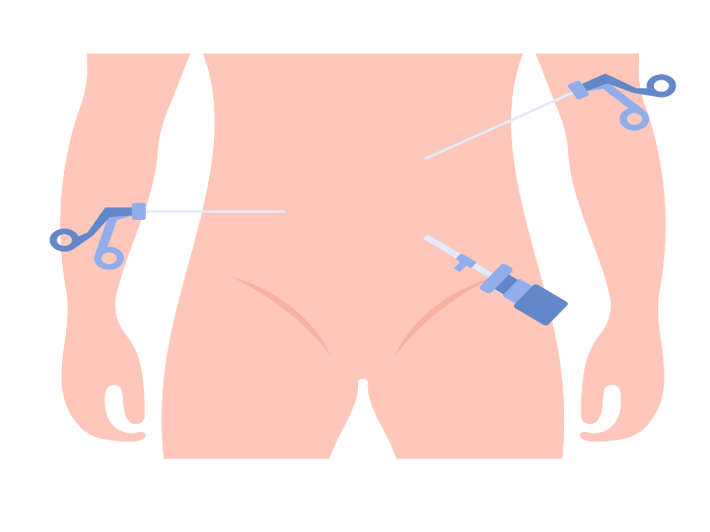
A laparoscopic appendectomy is a minimally invasive surgery used to remove an inflamed appendix. Instead of a large incision (5–10 cm) used in traditional open surgery, this procedure involves 1–3 small incisions, each about 1 cm long. Through these incisions, the surgeon inserts surgical instruments and a tiny camera to perform the surgery with precision. (1)
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery: (2)
- Less pain after surgery
- Faster recovery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Smaller scars
Sometimes, open surgery may still be necessary depending on the severity of the appendicitis.
Are There Alternatives to Surgery?
Surgery is the only definitive treatment for acute appendicitis. In some mild cases or for children, antibiotics may be used as a temporary alternative, but there is a higher chance that the inflammation may return. (3)
How Is the Procedure Performed?
A laparoscopic appendectomy usually takes about 1 hour and involves the following steps: (4)
- 1–3 small incisions are made in the abdomen.
- A thin tube is inserted, and carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdomen, creating space for the surgeon to work.
- A laparoscope (camera) and surgical tools are inserted to locate and remove the appendix.
- The incisions are closed with stitches, surgical staples, or covered with a dressing or Steri-Strips.
In some cases, the surgeon may switch to open surgery if the appendix is severely inflamed or the infection has spread.
At Al Ahli Hospital, our experienced surgical team uses the latest laparoscopic techniques to ensure safe, precise, and high-quality care.
Risks of Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Laparoscopic appendectomy is generally safe, but like all surgeries, it carries some risks: (2)
- Bleeding or infection
- Respiratory issues or blood clots
- Hernia at incision sites
- Heart complications
Possible post-surgery complications:
- Abscess formation in the abdomen, which may require another surgery to drain
- Rarely, injury to nearby organs or intestinal obstruction (2,5)
Recovery After Surgery
Hospital Stay:
Most patients go home the same day or the day after surgery. (3)
Pain Management:
Pain is usually mild and can be controlled with medications like paracetamol or ibuprofen. Some patients may experience shoulder pain due to leftover gas used to inflate the abdomen; walking and moving gently can help reduce this. (6)
Wound Care:
- Gently dry the incision after showering.
- Allow the area to breathe as much as possible.
- Avoid swimming or hot baths until the wound fully heals.
- Do not apply creams unless prescribed.
- Let dressings or stitches fall off naturally or follow your surgeon’s instructions.
- Wear loose clothing around the incision.
- Watch for signs of infection: redness, pain, foul discharge, bleeding, or warmth. (6)
Diet:
- Eat normally once nausea subsides; start with light meals if necessary.
- Drink 8–10 glasses of water daily.
- Focus on high-fiber foods to prevent post-surgery constipation. (3)
Activity:
- Walk and move gently as soon as possible.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects (over 4 kg) for at least 3–5 days.
- Ask your surgeon when it is safe to return to work. (6)
References
- ACS - Appendectomy
- SAGES - Appendix Removal (Appendectomy) Surgery Patient Information
- ACS - Appendectomy (PDF)
- Cleveland Clinic - Appendectomy
- Betterhealth - Appendectomy
- Michigan Medicine - Caring for myself after Laparoscopic Appendectomy