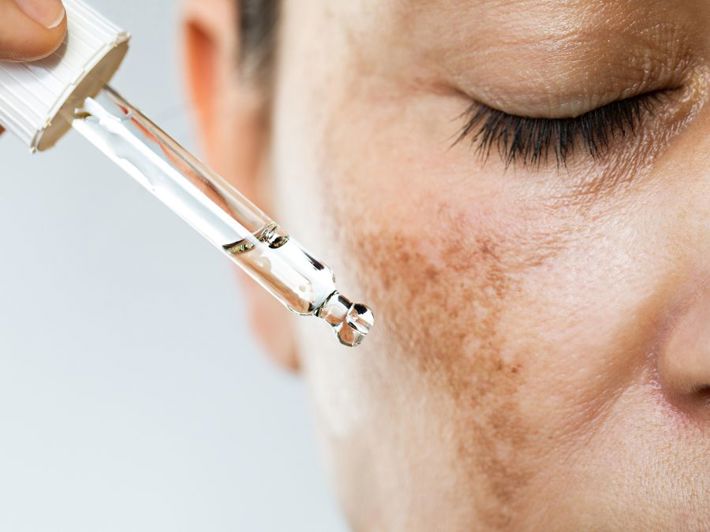
Skin pigmentation is a common dermatological issue that occurs when melanin production in the skin increases beyond normal levels, leading to the appearance of dark spots and an uneven skin tone.
There are many types and causes of pigmentation, such as melasma, sun spots, freckles, and age spots. While pigmentation is usually harmless, it can be frustrating for those who desire clear and even-toned skin. (1)
Treatments for Skin Pigmentation
Although pigmentation is not usually a medical concern, it’s often viewed as a cosmetic problem. Here are the most effective treatments to reduce hyperpigmentation:
Topical Creams
Topical treatments are usually the first line of defense because they’re convenient and effective. However, it’s important to consult a dermatologist before using any cream. These products contain active ingredients that lighten the skin and fade pigmentation. Common ingredients include: (2)
- Hydroquinone (e.g., Hi-Quin): A powerful skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production. Should be used under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
- Arbutin: A natural derivative of hydroquinone, known for being gentler and safer for the skin.
- Skin-lightening and exfoliating acids: Such as azelaic acid, kojic acid, and glycolic acid.
- Corticosteroids: Sometimes used in mild concentrations to reduce inflammation caused by other treatments.
- Retinoids (e.g., Acretin): Help renew skin cells and improve texture.
- Niacinamide: Reduces the transfer of melanin to the skin’s surface, helping to lighten dark spots.
In some cases, dermatologists may prescribe a combination of creams for enhanced results. One popular combination is the “triple therapy”: hydroquinone for lightening, tretinoin for cell turnover, and a mild corticosteroid (e.g., Alphacort) to reduce irritation. This treatment is typically prescribed for a limited duration and must be paired with strict sun protection. (1)
Chemical Peels
- How it works: Chemical peels use acids to exfoliate the skin’s surface and remove pigmented cells.
- Effectiveness: Peels are the second most common option for treating pigmentation, especially when topical treatments are insufficient. Dermatologists often combine chemical peels with creams for better results.
- Types: There are several types of peels—superficial, medium, and deep—chosen based on skin needs and pigmentation severity.
- Sessions: Patients typically require a series of sessions spaced a few weeks apart. (3)
Laser Treatments
- Effectiveness: Laser therapy is generally the third-line treatment, especially for deep pigmentation that doesn’t respond well to creams or chemical peels.
- Laser Types and Mechanism: The appropriate laser depends on skin tone and pigmentation depth, as not all lasers are safe for darker skin. Common types include:
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Uses a broad spectrum of light to target pigmented spots. Less effective for deep melasma, more suitable for surface-level pigmentation.
- Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser: Effective for deeper pigmentation and safe for darker skin.
- Erbium:YAG Laser: Gently resurfaces the skin to remove pigmented layers. (2)
Microneedling
- How it works: (2)
Microneedling uses a device with ultra-fine needles to create micro-injuries in the skin. This stimulates collagen production and enhances the absorption of serums used during the treatment.
Typically, brightening serums are applied during the procedure for better results.
- Effectiveness: Microneedling is often part of a broader protocol for treating pigmentation, improving overall skin tone and texture.
Important Recommendations
- Sun protection is essential: During and after any treatment to prevent further pigmentation.
- Consult a dermatologist: To determine the best treatment based on your skin type and pigmentation severity.
- Combination therapy: Often, the best results are achieved when treatments are combined (e.g., topical creams with chemical peels or laser).
All treatments should be supervised by a qualified dermatologist. For expert care and advanced solutions, visit the Dermatology Department at Al-Ahli Hospital in Qatar.
Are Home Remedies Effective for Pigmentation?
Home remedies may help with mild pigmentation, but they are not effective as standalone treatments, especially for more severe cases. (4)
Some popular natural ingredients include:
- Licorice extract: Reduces inflammation and lightens the skin.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and brightening properties.
- Green tea extract: Rich in catechins that reduce melanin production.
- Lemon: Contains vitamin C, which can help brighten the skin.
- Natural oils: Such as argan oil, jojoba oil, and rosehip oil.
Before trying any natural treatment, it’s crucial to test it on a small area first. Stop using it immediately if it causes irritation.
Note: Natural doesn’t always mean safe—some ingredients like lemon or turmeric can worsen skin sensitivity or existing conditions if used improperly.
References